Understanding Forceps-Assisted Births
What is a Forceps Delivery?
A forceps delivery is a method used during childbirth to help guide a baby out of the birth canal. Forceps are shaped like large tongs and are used when a baby is having trouble being born. The doctor carefully places the forceps around the baby’s head and helps pull the baby out while the mother pushes during contractions.
When are Forceps Used?
Forceps are typically used in situations such as:
- The baby shows signs of fetal distress, like an abnormal heartbeat.
- The mother is pushing but labor is not progressing.
- The mother has health issues, like high blood pressure, that make pushing difficult.
- The baby is stuck in the birth canal and needs assistance.
Types of Forceps Used During Delivery
There are different types of forceps that doctors may use, including:
- Low cavity/mid-cavity forceps – Used when the baby is lower in the birth canal.
- Outlet forceps – Used when the baby’s head is at the opening of the birth canal.
- Rotational forceps – Help turn the baby if they are in a sideways position.
Using forceps can be beneficial, but it is crucial that they are used correctly to avoid injuries. Improper use can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby. For more information on the risks associated with forceps deliveries, families may want to consult a forceps injuries lawyer to understand their options and rights.
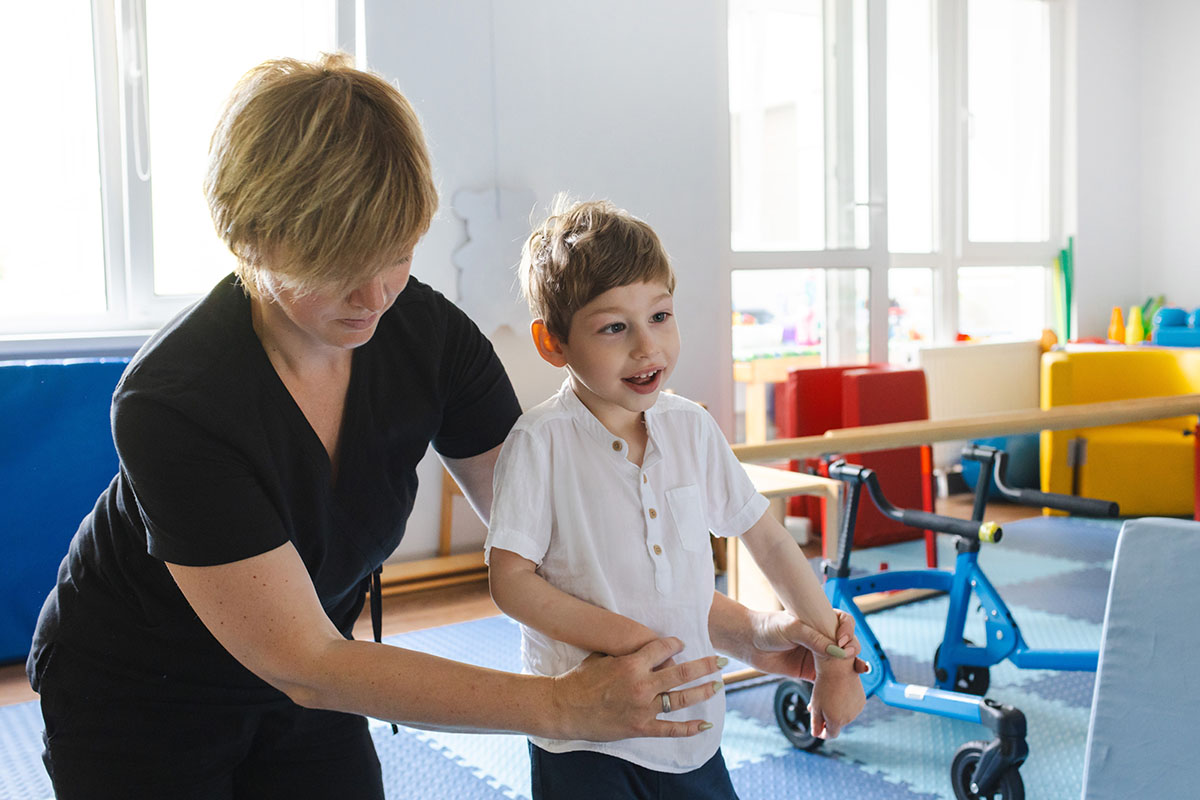
Common Injuries to Newborns from Forceps-Assisted Births
Forceps-assisted deliveries can sometimes lead to injuries in newborns. Understanding these potential injuries is crucial for parents and caregivers. Here are some common injuries that may occur:
Brain Injuries and Cerebral Palsy
- Cerebral Palsy: This is a serious condition that can result from pressure on the baby’s brain during delivery. It can lead to difficulties with movement and coordination.
- Bleeding in the Skull: This can happen if the forceps are used improperly, causing blood vessels to break.
- Seizures: Some babies may experience seizures due to brain injuries sustained during delivery.
Skull Fractures and Bone Injuries
- Skull Fractures: The forceps can apply too much pressure, leading to fractures in the skull.
- Broken Bones: Other bones, especially in the arms and shoulders, can also be broken during a forceps delivery.
Facial Injuries and Lacerations
- Facial Lacerations: The forceps can cause cuts on the baby’s face, which may require medical attention.
- Temporary Facial Weakness: Sometimes, the pressure from the forceps can lead to temporary weakness in the facial muscles, known as facial palsy.
Nerve Damage and Paralysis
- Brachial Plexus Injury: This occurs when the nerves in the arm are damaged, often leading to weakness or paralysis in one arm.
- Other Nerve Injuries: Other types of nerve damage can also occur, affecting the baby’s movement and sensation.
In summary, while forceps can be a helpful tool during delivery, they also carry risks that can lead to serious injuries for newborns. Awareness of these potential injuries can help in making informed decisions during childbirth.
Risk Factors for Forceps Delivery Complications
Maternal Health Conditions
Certain health issues in the mother can increase the chances of complications during a forceps delivery. These include:
- High blood pressure: This can make pushing difficult and risky.
- Heart disease: It may prevent the mother from safely exerting effort during labor.
- Diabetes: This can lead to larger babies, making delivery more challenging.
- Obesity: Extra weight can complicate the delivery process.
Fetal Position and Size
The position and size of the baby can also affect the safety of a forceps delivery. Key factors include:
- Baby’s position: If the baby is not facing the right way, it can be harder to deliver.
- Size of the baby: Larger babies may not fit easily through the birth canal, increasing the risk of injury.
- Multiple births: Delivering twins or more can complicate the use of forceps.
Prolonged Labor and Fetal Distress
When labor takes too long or the baby shows signs of distress, forceps may be considered. Important points are:
- Long labor: If the mother has been in labor for a long time, both she and the baby may be at risk.
- Fetal distress: If the baby’s heartbeat is abnormal, quick action may be needed, which can lead to the use of forceps.
Understanding these risk factors can help in making informed decisions during childbirth.
Preventing Injuries from Forceps-Assisted Births
Proper Training for Medical Professionals
To ensure the safety of both mother and baby during a forceps delivery, it is crucial that medical professionals receive proper training. This includes:
- Understanding the correct techniques for using forceps.
- Recognizing when forceps should be used and when they should be avoided.
- Being aware of the potential risks associated with forceps delivery.
When to Avoid Forceps Delivery
There are specific situations where using forceps can lead to serious injuries. Medical professionals should avoid forceps delivery if:
- The baby cannot fit through the mother’s pelvis.
- The baby has a bleeding disorder or weak bones.
- The baby is in an unknown position or leading with their arms.
Alternative Delivery Methods
In cases where forceps delivery may pose risks, healthcare providers should consider alternative methods. These can include:
- Emergency C-sections for safer delivery.
- Vacuum extraction, which uses a soft cup to help guide the baby out.
- Continuous monitoring of the baby’s heartbeat to assess distress and make timely decisions.
By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risk of forceps delivery and birth injuries.
Legal Recourse for Birth Injuries
Identifying Medical Negligence
When a newborn suffers an injury during a forceps-assisted delivery, it’s important to determine if medical negligence occurred. Here are some signs to look for:
- Improper Use of Forceps: If the doctor used forceps incorrectly or without proper training.
- Ignoring Risks: If the doctor knew the risks of using forceps but proceeded anyway.
- Failure to Monitor: If the medical team did not monitor the baby’s condition closely during delivery.
Filing a Lawsuit
If negligence is suspected, parents may consider filing a lawsuit. The steps typically include:
- Consulting a Lawyer: Speak with a lawyer who specializes in birth injuries.
- Gathering Evidence: Collect medical records and any other relevant documents.
- Filing the Claim: Your lawyer will help you file the lawsuit in the appropriate court.
- Negotiating a Settlement: Many cases are settled out of court, but some may go to trial.
Compensation for Birth Injuries
If a lawsuit is successful, families may receive compensation for various expenses, including:
- Medical Bills: Costs for treatments and therapies related to the injury.
- Future Care: Funds for ongoing care and support for the child.
- Emotional Distress: Compensation for the emotional impact on the family.
Long-Term Effects of Birth Injuries
Physical Disabilities
Birth injuries can lead to various physical disabilities that may affect a child’s ability to move and function normally. Some common issues include:
- Cerebral palsy, which can cause muscle control problems.
- Bone fractures that may heal but can lead to long-term mobility issues.
- Nerve damage, which can result in weakness or paralysis in certain body parts.
Cognitive and Developmental Issues
Injuries sustained during birth can also impact a child’s cognitive development. This may manifest as:
- Learning disabilities, making it hard for the child to keep up in school.
- Speech delays, affecting communication skills.
- Behavioral problems, which can lead to challenges in social interactions.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The effects of birth injuries are not just physical or cognitive; they can also have a significant emotional and psychological impact. Children may experience:
- Anxiety or depression, especially if they face ongoing challenges.
- Low self-esteem, stemming from difficulties in physical or social situations.
- Social isolation, as they may struggle to connect with peers due to their disabilities.
Overall, the long-term effects of birth injuries can be profound, affecting various aspects of a child’s life. Families may need to seek support and resources to help their child navigate these challenges effectively.